Версія даної теми для друку
Натисніть сюди для перегляду даної теми у оригінальному форматі
Розподілені обчислення в Україні _ Завершені проекти WCG _ Drug Search for Leishmaniasis
Автор: Rilian Aug 31 2011, 21:51

Проект "Drug Search for Leishmaniasis"
Проект запущен 31 Августа 2011
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- http://www.udea.edu.co/portal/page/portal/EnglishPortal/EnglishPortal
- http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/team/viewTeamInfo.do?teamId=J8H4J4QPN1
- http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/forums/wcg/listthreads?forum=520
- http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/research/dsfl/news.do
- http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/research/dsfl/faq.do
http://distributed.org.ua/forum/index.php?showtopic=890

----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Дата основания команды - 28.02.2005 Капитан - rilian
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
О проекте:
Mission
The mission of Drug Search for Leishmaniasis is to identify potential molecule candidates that could possibly be developed into treatments for Leishmaniasis. The extensive computing power of World Community Grid will be used to perform computer simulations of the interactions between millions of chemical compounds and certain target proteins. This will help find the most promising compounds that may lead to effective treatments for the disease.
Significance
Leishmaniasis is one of the most neglected tropical diseases in the world. Each year this disease infects more than two million people in 97 countries. To date, there are no available vaccines to prevent the disease, in spite of multiple research efforts. Leishmaniasis is caused by a protozoan parasite (genus Leishmania) transmitted between human and animal hosts by female sand flies. One form of the disease, the "visceral" form caused by Leishmania infantum in America, mainly affects children, who can die if adequate treatment is not provided promptly. Existing control measures rely upon drug therapy, insect control and education in the affected communities. However, the number of human cases continues to increase in tropical countries such as Bangladesh, India, Sudan, Ethiopia, Brazil, Colombia, Peru and many others.
The classical treatments for all forms of Leishmaniasis can cause severe side effects, including death. Furthermore, drug resistant parasites are causing major problems in many endemic countries. For these reasons, there is an urgent need for new, safe and inexpensive anti-Leishmania drug compounds.
Approach
A software program called VINA from The Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, California, will be used to perform the virtual chemistry experiments. These virtual experiments will search to find which of millions of drug compounds might be able to disable particular proteins, essential for the parasite's survival. Screening for the best potential drug compounds is an early step in the process of developing effective treatments for the disease. With enough computing power, this screening can be done much more quickly than using conventional laboratory experiments. However, existing computer facilities available to the researchers would require approximately 120 years to perform the screening. The power of World Community Grid can reduce the time required to less than one year. Information about the best candidate compounds will be published by the scientists, and this information will be available in the public domain for other scientists to build upon with their research. Further laboratory work using the best candidates identified by this project could lead to the development of better drugs to fight Leishmaniasis.
 About the Project
About the ProjectLeishmaniasis is a tropical disease caused by a parasite transmitted by specific insects. Infections of this disease have been increasing - with over two million people affected last year. Existing treatments can have severe side effects, including death. Currently, pharmaceutical companies have not been investing in extensive research to combat this disease. Therefore, the researchers at the University of Antioquia in Medellín, Colombia, are running a project on World Community Grid to search for chemical compounds which may lead to new drugs for treating this disease.
Leishmaniasis is caused by a single celled protozoan parasite. The genus of this protozoan is Leishmania. It is transmitted between human and animal hosts via the female sand fly. In the Americas, the genus of the sand fly is Lutzomyia and elsewhere it is Phlebotomus. The insect injects humans or other animals with promastigotes, the infective stage of the parasite. Once injected into the skin, the promastigote infects immune system cells such as macrophages and other mononuclear phagocytic cells. Within these cells, the promastigote transforms into the tissue stage of the parasite, known as amastigote, which multiplies inside the cell by simple division, moving on to infect other phagocytic mononuclear cells. Various factors of the parasite and host determine which form of the diseases appears in the host. The insects become infected by sucking infected cells of the host during a blood meal. In the insect´s gut, the cells rupture releasing amastigotes, which are transformed back into promastigotes. They multiply and develop in the insect's gut. After several days, depending on the species, the parasites migrate to the mouthparts of the insect, where they are ready again to be transmitted to a host, during the next blood meal.
The disease has three clinical forms:
* cutaneous - affecting the surface skin consisting mostly of ulcerated lesions, warty lesions or spots.
* mucocutaneous - affecting mucous membranes, particularly from the nose, laryngeal and pharynx.
* visceral - affecting bone marrow or internal organs, such as the liver, spleen and lymph nodes. Symptoms can include anemia, clotting problems, weight loss, enlarging of the spleen, liver and lymph nodes.
The classical treatments for all forms of Leishmaniasis are certain compounds of pentavalent antimony (e.g. sodium stibogluconate and meglumine antimoniate). These compounds can have severe side effects, including death. Furthermore, drug resistant parasites are causing major problems in many endemic countries. Several additional drugs such as Pentamidine and Amphotericin B have been used with variable success, but these drugs also have serious side effects and are expensive and difficult to administer, limiting their use as drugs of choice. More recently, Miltefosine (an oral drug) has been used with variable success in Central and South America against cutaneous Leishmaniasis and for visceral Leishmaniasis in India. A phase IV trial of this drug in India has shown an increase in the relapse rate, indicating that drug resistance may develop quickly. The visceral form mainly affects children, who can die if adequate treatment is not provided promptly.
The complete genomes of several Leishmania species have been decoded and are providing information about proteins and processes essential for the survival of the parasite. Certain Leishmania proteins have been identified as targets using information about the genomes and through prior laboratory experiments and computational work. If drugs can be developed to disable these proteins, they may prove to be an effective treatment for the disease. The first step in drug development is to find chemical compounds which attach to the target protein in a manner that disables the protein's function, thus preventing the progression of the disease. To accelerate the search for potential drugs against Leishmaniasis, the computing power of World Community Grid will be used to screen millions of potential chemical compounds as possible drug treatment candidates. Instead of performing expensive and time-consuming laboratory experiments, simulations of these millions of experiments will be performed using the software running on World Community Grid's member computers.
A software program called VINA from The Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, California, will be used to perform the virtual chemistry experiments, more precisely known as molecular dockings. Molecular docking is the process of determining how well two chemical compounds (molecules) bind together. One of the molecules is designated as the target, in this case one of several proteins, essential for the parasite's survival. The other compound is from a collection of millions of compounds from various drug data bases, cataloging known compounds and their exact atomic structure. The docking experiments position the two compounds in all possible orientations and then compute the binding energy, which tells how well they stick together. If a compound binds to the target protein, it may be useful in disabling the function of that protein and thus reducing parasite multiplication and the progress of the disease.
The VINA calculations will be used to identify the most promising chemical compounds that may inhibit these proteins. The computer computations involved are very intensive and would take about 120 years to test the 12 million compounds against 70 Leishmania proteins, if using machines normally available to the researchers. World Community Grid will be able to reduce the time required to less than one year. Information about the best candidate compounds will be published by the scientists, and this information will be available in the public domain for other scientists to build upon with their research. Further laboratory work using the best candidates identified by the VINA computations could lead to the development of better drugs to fight Leishmaniasis.
Наименования рабочих заданий и их количество (обновлено 31 августа 2011)
Work unit numbering is in this format:
DSFL_TTTTTTTT_BBBBBBB_WWWW
T=Target
B=Batch
W=Work unit number
Сейчас кол-во целей (target) 5353, и в каждой 58 пачек (batch). В каждой пачке примерно 1000 заданий, с кворумом 2
Учитывая что время задания в среднем 6 часов, получаем 5353*58*1000*2*6= 3,725,688,000 часов = 425000 процессорных лет
Добавляя 6% на разные ошибки и таймауты, получается ~450000 процессорных лет, или 450000/345 = 1300 WCG дней (если бы считался только этот проект)
Команда
Stan Watowich, The University of Texas Medical Branch (Galveston, Texas, USA) -- помошник, координатор DDDT2
Carlos Muskus, PECET, University of Antioquia, Medellín, Colombia
Andres Florez, PECET, University of Antioquia, Medellín, Colombia
Rodrigo Ochoa, PECET, University of Antioquia, Medellín, Colombia
Ссылки по теме:
- http://renewables.ru/modules.php?name=PagesAd&pa=showpage&pid=43
Видео о проекте (http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/bg/video/dsfl_svga.mpg)
Как выглядит графический клиент:
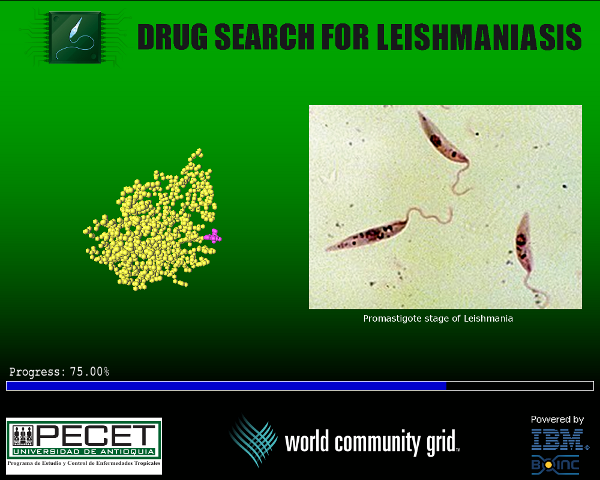
График работы проекта

Автор: tiss Aug 31 2011, 21:54
Срачно переключил на этот проект свои мощности ![]()
Автор: Rilian Aug 31 2011, 21:56
Я теж. Змагаємось, хто швидше збере сапфіровий бейджик?
Порахую 2 рокі (на сапфір), і обратно на HCC
Автор: tiss Aug 31 2011, 21:58
Я тоже. Соревнуемся, кто первый соберет сапфир?
Дон Алексус смотрит на нас как...
Автор: Rilian Aug 31 2011, 22:01
ВЮ займає 70МБ пам'яті
непогано ![]()
Я тоже. Соревнуемся, кто первый соберет сапфир?
Дон Алексус смотрит на нас как...
http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/stat/viewMemberInfo.do?userName=Alexus78 кранчіт HCC, за що йому величезний респект і уважуха!
Автор: Bel Aug 31 2011, 22:14
Порахую 2 рокі (на сапфір), і обратно на HCC
Да там уже как кот наплакал тех заданий. Скоро можно добить HCC, и переключаться на что то другое.
Автор: Rilian Aug 31 2011, 22:26
Додав у шапку інформацію про кількість та довжину РЗ (робочих завдань)
Автор: Rilian Aug 31 2011, 22:37

Автор: Rilian Sep 5 2011, 15:09
Отримав бронзу! 
нажаль сьогодні було виявлено помилки в таргетах 6-8, і зараз проект видає дуже мало завдань -- для тестування -- таргетів 9-15
Рекомендую, якщо ви переключились сюди, додати HCC як запасний проект
Автор: Rilian Sep 5 2011, 15:14
ти крут! чекаємо першого командного сапфіра
Автор: Brodyaga Sep 6 2011, 10:41
Задания в этом проекте примерно одинакового размера (в смысле по времени, необходимого для вычисления одного задания) или разные?
Автор: Rilian Sep 6 2011, 11:16
Задания в этом проекте примерно одинакового размера (в смысле по времени, необходимого для вычисления одного задания) или разные?
однакові, орієнтуються на 6 годин
в кожному РЗ є 40 підзавдань
Автор: london2004 Sep 6 2011, 14:39
У меня есть задания и по 10 и по 18 часов
Автор: Rilian Sep 7 2011, 10:28
завдання з 7 таргета можуть бути дуже довгими. Але все ок
Thanks,
-Uplinger
Автор: Rilian Sep 7 2011, 18:22
Розсилка про проект!
http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/about_us/viewNewsArticle.do?articleId=170
Launch of the Drug Search for Leishmaniasis Project
Category: Drug Search for Leishmaniasis
Tags: Accomplishments , Project Update , Project Event
Summary
World Community Grid is pleased to announce the launch of the Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project.
This project is provided by the University of Antioquia in Medellín, Colombia, with assistance from researchers at the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston, Texas. This project hopes to identify potential molecule candidates that could possibly be developed into treatments for Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is one of the most neglected tropical diseases in the world. Each year this disease infects more than two million people in 97 countries. To date, there are no available vaccines to prevent the disease.
Existing control measures rely upon drug therapy, insect control and education in the affected communities. However, the number of human cases continues to increase in tropical countries such as Bangladesh, India, Sudan, Ethiopia, Brazil, Colombia, Peru and many others.
The classical treatments for all forms of Leishmaniasis can cause severe side effects, and even lead to death. Furthermore, drug resistant parasites are causing major problems in many endemic countries. For these reasons, there is an urgent need for new, safe and inexpensive anti-Leishmania drug compounds.
A software program called VINA from The Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, California, will be used to perform the virtual chemistry experiments. These virtual experiments will search to find which of millions of drug compounds might be able to disable particular proteins, essential for the parasite's survival. Screening for the best potential drug compounds is an early step in the process of developing effective treatments for the disease. With enough computing power, this screening can be done much more quickly than using conventional laboratory experiments.
For additional information on this project, please press the Research button in the upper navigation bar or http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/research/dsfl/overview.do.
Participation in the Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project
Drug Search for Leishmaniasis is the eighteenth research project to be launched on World Community Grid and one of nine projects currently running on World Community Grid. The other eight research projects are:
Computing for Clean Water (launched August, 2010)
The Clean Energy Project – Phase 2 (launched June, 2010)
Discover Dengue Drugs – Together – Phase 2 (launched February, 2010)
Help Cure Muscular Dystrophy – Phase 2 (launched May, 2009)
Help Fight Childhood Cancer (launched March, 2009)
Help Conquer Cancer (launched November, 2007)
Human Proteome Folding - Phase 2 (launched July, 2006)
FightAIDS@Home Phase 2 (launched November, 2005)
For more detailed information and FAQs about each of these projects, please click on the Research button in the upper navigation bar. We thank all of our members for their valuable contributions to the projects to date and hope you will continue to help us process those, as well as this latest project.
Because there are nine research projects running on World Community Grid, your grid agent could receive work units from any of the projects depending on your Project profile. If you prefer, you may elect to focus your computer's time only on particular projects. To do so, press the My Grid button in the upper navigation bar and select My Projects or https://secure.worldcommunitygrid.org/ms/viewMyProjects.do. Work is sent only to machines which meet minimum system requirements set for a particular project. To read more specifics on the system requirements for the Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project and the other projects, http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/help/viewTopic.do?shortName=minimumreq.
Project Badge 
If a member contributes a minimum of 14 days of CPU Run Time to this project, they will receive a Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project badge on their member statistics page and next to their member name when they post in the forums. There is a different badge for each research project and beta testing. To read more about badges, http://worldcommunitygrid.org/help/viewSearch.do?searchString=Badges.
Forums
In addition to providing information about this project, we have created a forum for discussions about the Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project. To participate in this forum, please press the Forums button in the upper navigation bar orhttp://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/forums/wcg/listthreads?forum=520. Only forum authors with the title "Drug Search for Leishmaniasis Scientist" are authorized to comment as representatives of the University of Antioquia in Medellín, Colombia.
Questions?
If you have any questions, World Community Grid provides you with four methods of obtaining assistance: (1) Review the FAQs found in the http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/help/viewHelp.do section of the website; (2) Review the forums to see if anyone has asked/answered the question that you have; (3) Ask the question in World Community Grid's Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project forum found http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/forums/wcg/listthreads?forum=520 and a Community Advisor or a more experienced member will provide an answer; or (4) Send an email to the support desk from the http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/viewContactUs.do link found at the bottom of every page of the website (except in the forums).
We thank you for contributing to the Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project. ![]()
Всім приємних розрахунків на користь людства!
Автор: tiss Sep 7 2011, 18:29
Розсилка про проект!
А у меня уже золотой беджик
Автор: Rilian Sep 8 2011, 10:21
Leishmaniasis is one of the most neglected tropical diseases. Each year it infects more than two million people in 97 countries. To date, there are no available vaccines to prevent the disease. Researchers at the University of Antioquia in Medellin, Colombia, are running the http://distributed.org.ua/forum/index.php?showtopic=5269 project on http://distributed.org.ua/forum/index.php?showforum=55 to identify drug compounds that could possibly be developed into treatments for Leishmaniasis.
Автор: Salmonella Sep 9 2011, 05:25
Что-то все вдруг вспомнили про "забытые" болезни. Модный тренд не иначе. ![]() Полез к Д. Бейкеру на сайт, и у них там в разделе "Structure-Based Drug Design". Внезапно:
Полез к Д. Бейкеру на сайт, и у них там в разделе "Structure-Based Drug Design". Внезапно: ![]()
Larson E.T., Kim J.E., Castaneda L.J., Napuli A.J., Zhang Z., Fan E., Zucker F.H., Verlinde C.L.M.J., Buckner F.S., Van Voorhis W.C., Hol W.G.J., Merrit E.A. (2011). Tyrosyl tRNA-synthetase from the eukaryote Leishmania major is monomeric but forms an intrinsically asymmetric pseudo-dimer. J. Mol. Biol. 409: 159-176. [PMID: 21420975]
Shibata S., Gillespie J.R., Kelley A.M., Napuli A.J., Zhang Z., Kovzun K.V., Pefley R.M., Lam J., Zucker F., Van Voorhis W.C., Merritt E.A., Hol W.G.J., Verlinde C.L.M.J., Fan E., Buckner F.S. (2011). Selective inhibitors of methionyl-tRNA synthetase have potent activity on Trypanosoma brucei infection in mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55: 1982-1989. [PMID: 21282428]
Merritt E.A., Arakaki T.L., Gillespie R., Napuli A.J., Kim J.E., Buckner F.S., Van Voorhis W.C., Verlinde C.L.M.J., Fan E., Zucker F., Hol W.G.J. (2011). Crystal structures of three protozoan homologs of tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol.177: 20-28. [PMID: 21255615]
Ojo K.K., Arakaki T.L., Napuli A.J., Kishore K., Keyloun K.R., Zhang L., Hol W.G.J., Verlinde C.L.M.J., Merritt E.A. Van Voorhis W.C. (2011). Structure Determination of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 from Leishmania major Explains a Distinct Inhibitor Structure Activity Relationship Compared with Trypanosoma brucei GSK-3. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol.176: 98-108. [PMID: 21195115]
Larson E.T., Kim J.E., Zucker F., Kelley A., Mueller N., Napuli A.J., Verlinde C.L.M.J., Fan E., Buckner F.S., Van Voorhis W.C., Merritt E.A., Hol W.G.J. (2011). Structure of Leishmania major methionyl-tRNA synthetase in complex with intermediate products methionyladenylate and pyrophosphate. Biochimie 93: 570-582. [PMID: 21144880]
Автор: Rilian Sep 9 2011, 10:41
Salmonella, дай посилання. не знайшов на сайті Розетти
Автор: Salmonella Sep 9 2011, 12:17
Это на факультете у Бейкера на сайте Университета. Тыкал ссылки. ![]() А Бейкера приплёл потому что он Гуру.
А Бейкера приплёл потому что он Гуру. ![]() Забавно, получилось, практически все статьи по Лейшманиозу за 2011 год, за другие года - почти ничего. Случайность если хотите.
Забавно, получилось, практически все статьи по Лейшманиозу за 2011 год, за другие года - почти ничего. Случайность если хотите. ![]()
Вашингтонский универ тоже протозойными болезнями занимается.
http://www.sgpp.org/members.shtml
http://www.msgpp.org/members.shtml
http://depts.washington.edu/bmsd/people/faculty.php
Автор: Rilian Sep 30 2011, 15:33
Накранчил на рубин 
Автор: Khvastov Maxim Sep 30 2011, 15:43
Мне вот бронза капнула  - мелочь, а приятно
- мелочь, а приятно ![]()
![]()
Автор: london2004 Sep 30 2011, 17:47
Уже вернулся отсюда на НСС, там очков меньше, но вроде нужнее.
Автор: KING100N Sep 30 2011, 17:50
Уже вернулся отсюда на НСС, там очков меньше, но вроде нужнее.
Там проект через 20 дней закончится. Устроим финишный спурт?
Автор: Rilian Sep 30 2011, 18:06
Уже вернулся отсюда на НСС, там очков меньше, но вроде нужнее.
мне тут подкинули 16-ядерную машину (по 2 ггц) - на ней быстро бейджики зарабатываются - по 20 дней в день. Потом сразу обратно на ХЦЦ
Автор: Rilian Oct 11 2011, 10:26
пока я переключился на HCC + HFCC для соревнования, у меня навалидировалось ВЮх на изумруд (1 год)
Вернусь сюда в ноябре, добить еще 1 год для сапфира
Автор: Rilian Apr 16 2012, 17:28
04 Apr 2012
The scientists working on the Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project on World Community Grid have written a chapter in the book "Current Topics in Tropical Medicine".
A link to this open science book can be found here: http://www.intechopen.com/books/current-topics-in-tropical-medicine
Chapter 16, entitled "Current Advances in Computational Strategies for Drug Discovery in Leishmaniasis", describes the scientific details of identifying drug targets and drug candidates and mentions how World Community Grid plays a role in the process. You may read the text of this chapter http://www.intechopen.com/books/current-topics-in-tropical-medicine/current-advances-in-computational-strategies-for-drug-discovery-in-leishmaniasis-.
Автор: Bel Apr 16 2012, 18:00
Серебряшку накранчил. 
![]()
Автор: Rilian Jun 6 2012, 14:49
С этого момента в проекте кворум = 1 ![]()
Автор: Rilian Jul 12 2012, 11:02
Thanks for all people supporting the DSFL project
Dear WCG members.
This is a short message just to thanks all members (crunchers) of the WCG supporting the project Drug Search for Leishmaniasis (DSFL) for the almost 19 millions results processed and returned to the World community grid out of the 1 billion results results. Hope we can continue receiving this help to try to get a new safe and cheap drug for the leishmaniasis treatment.
Best wishes from Colombia and thanks again
Автор: Death Jul 12 2012, 11:46
19 millions results processed and returned to the World community grid out of the 1 billion results results
то есть 1.9% посчитали?
Автор: Rilian Jul 12 2012, 11:48
19 millions results processed and returned to the World community grid out of the 1 billion results results
то есть 1.9% посчитали?
нет, просто недавно ВЦГ преодолели рубеж в 1 МЛРД посчитанных заданий, из них 1.9% это ДСФЛ
Автор: Rilian Jul 26 2012, 10:37
Апдейт проекта
Drug Search for Leishmaniasis Update
Rodrigo Ochoa and Carlos Muskus
The project “Drug Search for Leishmaniasis” has been running during 10 months, and the following is a brief description of our progress and what have been validated until now:
The original project included the evaluation of 53 crystallized Leishmania proteins obtained from the PDB database along with 5,300 modelled structures, (100 modelled structures for each protein downloaded from PDB) (figure 1). The modelling was carried out through Molecular Dynamics using the NAMD program, representing an indirect way to provide flexibility for each one of the potential targets.
However, based on the statistic of the project after 6 months of activity, to run the 5.353 protein structures against the 600.000 compounds will spend around 20-25 years to complete. These made us to reconsider the project just prioritizing 10 structures for each of the 53 proteins for a total of 530 structures (Phase 2). Originally the idea was to build a molecular trajectory using snapshots of a protein during a computational simulation, trying to mimic the biological environment of the protein inside the organism. The trajectories contain 100 snapshots. Nevertheless, to prioritize the data, 10 snapshots per trajectory (i.e from the 100 structures per protein, the snapshots 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80 90 and 100 were selected) (see figure 2). That rational selection pretends to cover substantial changes in the conformation of the binding site of the protein.
Currently, WCG have processed approx. 76.200.000 docking simulations (127 structures against 600.000 compounds in phase I). From the second phase, it has processed approx. 37.800.000 docking simulations (63 priority structures against the same 600.000 compounds). Due to the huge amount of data, only the top 20 compounds per structure (compounds with the best score hits) and based on the score function proposed by the AutoDock VINA software, have been extracted. As an example, we provided the top 20 compound which lists from the protein 1-10, 1-20 and 1-30* (See tables 1, 2 and 3)
*The notation 1-10 means the modelled structure 10, from the protein target 1 of the 53 original proteins downloaded from PDB database.
A future analysis with the high relevant results will be published in the next update of the project.

Figure 1. Representation of the 53 original PDB proteins (black-red squares at the bottom), and the 5300 (blue squares) modelled proteins. Solid Red squares along with the black-red squares represent 127 proteins that were already docked against the 600.000 compounds in the first phase of the project

Figure 2. Priority targets (530 structures) are represented by solid red squares and are being docked against the 600.000 compounds. Modelled protein 1 is more similar in structure to the original proteins obtained from PDB than modeled protein structure 100. Sixty three priority structures out of the 530 have been already docked against the 600.000 compounds.
Table 1. Top 20 docking results for modelled structure 10 from the protein target number 1.

Table 2. Top 20 docking results for modelled structure 20 from the protein target number 1.

Table 3. Top 20 docking results for modelled structure 30 from the protein target number 1.

http://pecet-colombia.org/worldcommunitygrid/drugsearch/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=11%3Adrug-search-for-leishmaniasis-update&catid=1%3Aeventos&Itemid=6&lang=en
Автор: Bel Aug 25 2012, 09:50
Среднее время выполнения всех заданий увеличилось на 20%!
Автор: Rilian Nov 1 2012, 12:11
Current status of the Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project
When we initially launched the project in September 2011 on World Community Grid, we planned on using Autodock-Vina to evaluate the docking of 5,353 protein structures from the Leishmania parasite against 600,000 chemical compounds selected and filtered from the ZINC database. The software measures the protein-compound interaction in a three dimensional space and generates a score according to the degree of affinity. The 5,353 protein structures correspond to 53 Leishmania proteins for which the crystal structures were obtained from x-ray crystallography information found in the http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/home/home.do along with 100 alternate modeled protein structures for each of the 53 original structures. However, the rate of progress showed that it would take 20-25 years to compute all of these interactions. Therefore we prioritized the 5,353 structures and focused on just 530 modeled structures along with the 53 original PDB structures for a total of 583 structures. This would give us useful results much sooner.
The table loaded in the http://pecet-colombia.org/worldcommunitygrid/drugsearch/index.php?option=com_content&view=section&layout=blog&id=1&Itemid=6&lang=en summarizes the status of the DSFL project. Each of the cells on the table corresponds to any of the 5,353 structures, both original and modeled. The green cells correspond to the 53 original structures from PDB (bottom horizontal row) and 75 modeled structures of the first PDB protein (first column) already docked before prioritizing the 530 structures. The blue cells correspond to the 530 modeled and prioritized structures that have been already docked against the 600,000 compounds. And finally, the red cells correspond to those 530 priority structures pending to be processed.
We give a very big “thank you” to the World Community Grid members for contributing to this project!
Кратко: всего надо ісследовать взаімодействіе 5353 белков, із ніх 530 рассчітиваются с большім пріорітетом так как оні важнее. В таблічке видно существующий прогресс 
http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/forums/wcg/viewthread_thread,34157
Автор: Sonechko Feb 7 2013, 20:01
Sapphire - done ![]()

Автор: Rilian Mar 26 2013, 14:38
Апдейт проекта
посчитано 67%
Drug Search for Leishmaniasis Update
Rodrigo Ochoa and Carlos Muskus
The project “Drug Search for Leishmaniasis” has been running during 10 months, and the following is a brief description of our progress and what have been validated until now:
The original project included the evaluation of 53 crystallized Leishmania proteins obtained from the PDB database along with 5,300 modelled structures, (100 modelled structures for each protein downloaded from PDB) (figure 1). The modelling was carried out through Molecular Dynamics using the NAMD program, representing an indirect way to provide flexibility for each one of the potential targets.
However, based on the statistic of the project after 6 months of activity, to run the 5.353 protein structures against the 600.000 compounds will spend around 20-25 years to complete. These made us to reconsider the project just prioritizing 10 structures for each of the 53 proteins for a total of 530 structures (Phase 2). Originally the idea was to build a molecular trajectory using snapshots of a protein during a computational simulation, trying to mimic the biological environment of the protein inside the organism. The trajectories contain 100 snapshots. Nevertheless, to prioritize the data, 10 snapshots per trajectory (i.e from the 100 structures per protein, the snapshots 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80 90 and 100 were selected) (see figure 2). That rational selection pretends to cover substantial changes in the conformation of the binding site of the protein.
Currently, WCG have processed approx. 76.200.000 docking simulations (127 structures against 600.000 compounds in phase I). From the second phase, it has processed approx. 37.800.000 docking simulations (63 priority structures against the same 600.000 compounds). Due to the huge amount of data, only the top 20 compounds per structure (compounds with the best score hits) and based on the score function proposed by the AutoDock VINA software, have been extracted. As an example, we provided the top 20 compound which lists from the protein 1-10, 1-20 and 1-30* (See tables 1, 2 and 3)
*The notation 1-10 means the modelled structure 10, from the protein target 1 of the 53 original proteins downloaded from PDB database.
A future analysis with the high relevant results will be published in the next update of the project.
Figure 1. This new graph represent the current progress of the 583 priority targets (530 modelled proteins + 53 original structures) docked against the 600.000 compounds. The red bar at the botton of the figure represents the 53 original proteins structures already docked. The others bars represent the modelled protein structures (from 10 to 100). The blue color areas represent modelled proteins already docked and the green color areas represent the modelled proteins pendindg for docking. As you can see there are 203 modelled structures pending for docking which correspond to approximately 35%.
http://pecet-colombia.org/worldcommunitygrid/drugsearch/index.php?option=com_content&view=section&layout=blog&id=1&Itemid=6%E2%80%9E%C3%84%C3%A0=
Автор: Rilian Apr 13 2013, 11:09
DSFL update - April 11, 2013
With your help or contribution, 71% of the priority proteins have been processed against the 600.000 compounds. According to the statistic of the project, it is estimated to end in the middle of august this year.
An update of the project have been loaded in the project website: http://pecet-colombia.org/worldcommunitygrid/drugsearch/index.php?option=com_content&view=section&layout=blog&id=1&Itemid=6&lang=en
Thank to all of you for your collaborations.
The project “Drug Search for Leishmaniasis” has been running during 10 months, and the following is a brief description of our progress and what have been validated until now:
The original project included the evaluation of 53 crystallized Leishmania proteins obtained from the PDB database along with 5,300 modelled structures, (100 modelled structures for each protein downloaded from PDB) (figure 1). The modelling was carried out through Molecular Dynamics using the NAMD program, representing an indirect way to provide flexibility for each one of the potential targets.
However, based on the statistic of the project after 6 months of activity, to run the 5.353 protein structures against the 600.000 compounds will spend around 20-25 years to complete. These made us to reconsider the project just prioritizing 10 structures for each of the 53 proteins for a total of 530 structures (Phase 2). Originally the idea was to build a molecular trajectory using snapshots of a protein during a computational simulation, trying to mimic the biological environment of the protein inside the organism. The trajectories contain 100 snapshots. Nevertheless, to prioritize the data, 10 snapshots per trajectory (i.e from the 100 structures per protein, the snapshots 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80 90 and 100 were selected) (see figure 2). That rational selection pretends to cover substantial changes in the conformation of the binding site of the protein.
Currently, WCG have processed approx. 76.200.000 docking simulations (127 structures against 600.000 compounds in phase I). From the second phase, it has processed approx. 37.800.000 docking simulations (63 priority structures against the same 600.000 compounds). Due to the huge amount of data, only the top 20 compounds per structure (compounds with the best score hits) and based on the score function proposed by the AutoDock VINA software, have been extracted. As an example, we provided the top 20 compound which lists from the protein 1-10, 1-20 and 1-30* (See tables 1, 2 and 3)
*The notation 1-10 means the modelled structure 10, from the protein target 1 of the 53 original proteins downloaded from PDB database.
A future analysis with the high relevant results will be published in the next update of the project.

Figure 1. This new graph represent the current progress of the 583 priority targets (530 modelled proteins + 53 original structures) docked against the 600.000 compounds. The orange bar at the bottom of the figure represents the 53 original proteins structures already docked. The others bars represent the modelled protein structures (from 10 to 100). The blue color areas represent modelled proteins already docked and the green color areas represent the modeled proteins pending for docking. As you can see, there are 136 modelled structures still pending for docking which correspond to approximately 29%.
We want also to thank all the WCG members supporting this project all over the world, for the almost 19.000.000 results processed, out of the 1 billion data returned to the World Community Grid from IBM.
Автор: Rilian May 30 2013, 11:00
Сообщение описывает с медицинской точки зрения, почему проект ищет новые варианты противодействия, несмотря на то что цены на существующие аналоги падают.
Comments on amphotericn B and why seacrhing new drugs
Dear DSFL cruncher
Amphotericin B is a drug that have been used as a second choice for the Leishmaniasis treatment in many endemic areas and with good efficay. Initially, it was administered parenterally in those patients that did not respond to the antimonials. However, it could caused severe side effects and other times it was contraindicated for certain patients. Then it was encapsulated in liposomes (a lipid bag) and the severe side effect diminished, but it was expensive. Currently, the company manufacturing this presentation cut the price and it uses as antileishmania agent have been extended. However, in spite of it decrease in toxicity and price, in this liposome presentation, the administration have to be parenteral.
It is good to know that promising studies to administer amphotericin B orally are in course at least for Visceral Leishmaniasis, which is mainly caused by two Leishmania species (Leishamnia donovani and Leishmania infantum).
We have been testing an ointment presentation of amphotericin B, with also promising results, obviously for cutaneous leishmaniasis which are approximately 1.5 million cases per year.
But why to continue searching for new drugs??. Among several reason are:
1. The number of alternative options are few. We need more or alternative options
2. The efficacy of the current drugs (included amphotericin B) can be variable depend on the Leishmania species (there are more than 20 Leishmania species associated with disease in human).
3. Development of parasite resistance when administration of amphotericin B is authorized in most endemic countries as first option, is a probability. We have to be prepared to face it.
4. The administration of amphotericin B may be contraindicated in some patients with particular condition.
5. And why to administer a systemic drug with some toxicity for treating a cutaneous ulcer?.
6. Cost may be also a reason given Leishmaniasis is mostly endemic in poor countries or affecting poor communities.
There are even more reason.
Best wishes
carmusk
Drug Search for Leishmaniasis Scientists
Автор: Rilian Jun 8 2013, 19:38
07 Jun 2013
Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project update
Summary
A poster, containing preliminary Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project results, presented at the WorldLeish5 Congress in Porto de Galinhas-Brasil in May 2013.
The following Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project update can be found http://pecet-colombia.org/worldcommunitygrid/drugsearch/index.php?option=com_content&view=section&layout=blog&id=1&Itemid=6&lang=en .
Dear DSFL cruncher.
I am loading a poster with preliminary results from the DSFL project. This poster was presented in the past WorldLeish5 Congress in Porto de Galinhas-Brasil from May 13 to 17. Given this is the World Congress on Leishmaniasi and attended by the most important scientific working on Leishmaniasis from all over the world, I could see that none lab is doing an ambicious work like this in terms of searching new drugs for Leishmaniasis, and this has been possible for all your support as was mentioned in the acknowledge section of if. Some researchers attending the meeting and working in drug discovery were talking with me about the project and were a bit impressed. Thanks again and we are almost close to finish the project.
After we finish the computational work, we ill start the second part, which consist of filtering and selecting the potential candidates to test them in vitro and in vivo. The selection steps is based in the Autodock vina score, if the potential compound has human approval use, oral administration, cost, etc.
Best wishes and thanks
http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/about_us/viewNewsArticle.do?articleId=305
Автор: Rilian Jun 9 2013, 09:36
Осталось менее 100 дней до завершения проекта!
Спешите заработать бейджик! ![]()
![]()
Автор: Rilian Jun 18 2013, 12:04
по моим подсчетам 1 фаза проекта закончится где-то через 60 дней ![]()
Автор: MAGADAN Jun 18 2013, 15:30
Что у них резкий скачет пошол вниз по дням ![]()
И на этом проекте я могу пролететь с Сапфиром ![]()
Rilian если у меня щас 193 дня , и средняя 6 дней производительность я успею добраться до САПФИРА при условии что не будет разких скачков вниз по дням ?
Автор: Rilian Jun 18 2013, 15:50
MAGADAN, скачки резкие будут так как в ВЦГ щяс только 2 проекта работают в полную мощность. Этот и FAAH. То есть все 400 процессорных лет в день направлены сюда.
так что я бы рекомендовал все силы сюда направить если ты планируешь добраться до бейджика
Автор: Dromage Jun 18 2013, 15:50
Ну посчитай сам:
(356*2-193)/6=86,5 реальных суток
Автор: MAGADAN Aug 6 2013, 14:23
Усё ![]() http://worldcommunitygrid.org/forums/wcg/viewthread_thread,35490
http://worldcommunitygrid.org/forums/wcg/viewthread_thread,35490
Автор: Rilian Aug 6 2013, 15:06
Dear WCG members.
For us it is a pleasure to let you know that the computational process of the DSFL project has ended. We want to thanks all people for helping us to develop the project providing computational time and effort, and to the WCG team for the professional support to carry out this task. As I have mentioned before, without your help this project had been impossible to conduct in Colombia and probable in many countries all over the world.
Beside the initial 53 Leishmania proteins, we added a few more proteins that will be analyzed along with the first batch.
But I am sure one of your probable question is: and now what is next?:
There are several steps we have to travel through, and these are:
1. To identify the best ranked compounds in term of the docking score. Autodock Vina rank protein-compound interaction based in the energy of interaction and assign a score. The results of the project were organized in a large database built in MySQL language by Rodrigo Ochoa, one of the PECET team. The amount of information we already have in our NAS is about 6 terabytes, so it is not an easy task to look into such amount of data, which are the best candidates. In order to identify the best candidates, a script was created and it is currently running. We hope at the end this year or before, to have the complete list of potential anti-leishmanial compounds or molecules.
2. Depending on the number of potential compounds predicted with promising score, we have probably to filter them based on several parameters, like costs, administration route (oral, injected, topic), toxicity, human use approval for other diseases, etc.
3. Those filtered compounds will be evaluated in in vitro assays and those passing the in vitro phase will be tested in vivo.
4. Finally those passing in vitro and in vivo tests, will be evaluated in human clinical trials.
How long can it take??.
Probably years, To get an effective and safe drug, is not an easy task, but we hope to get one among the 600.000 you tested in your computers. We will let you know if we get any.
Best wishes and thanks again.
Автор: Rilian Oct 19 2013, 14:12
End of the Drug Search for Leishmaniasis Phase 1
Summary
A big thank-you from the research team as the Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project analyzes the results from grid computations.
A successful collaboration
For the past two years, World Community Grid members have been helping a research team from the University of Antioquia in Medellín, Colombia, simulate chemical compounds to see which ones might bind to key proteins in the Leishmania parasite. This is a crucial first step in developing a better treatment for this neglected tropical disease, which affects millions of people each year but gets very little research attention.
Thanks to the computing power you provided, the chemical binding simulations were completed earlier this year. The researchers have already started combing through the 7 TB of raw data provided by World Community Grid volunteers, to determine which of the potential molecules might become the basis for practical treatments. As Dr. Carlos Muskus explained in his recent forum posts, the analysis of the raw data has already revealed several promising compounds, and the next step is to complete the analysis phase and secure funding for in-vitro testing. Therefore, we can officially close Phase 1 of the Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project on World Community Grid.
The researchers send their thanks to the over 120,000 World Community Grid members who participated in this project. Together, you donated over 37,000 years of computing time and carried out almost 60 million calculations for this project. With your help, the researchers were able to analyze their original proteins, add several new proteins to the list of targets, and still cut the required completion time by more than 100-fold. Depending on the results of their work over the next several months, a second phase of the project may be started next year.
http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/about_us/viewNewsArticle.do?articleId=326
Автор: Arbalet Dec 9 2014, 19:34
Обработка результатов проекта Drug Search for Leishmaniasis в самом разгаре
Автор: Доктор Карлос Мускус Лопес (Carlos Muskus López), координатор проекта Drug Search for Leishmaniasis из Программы по изучению и борьбе с тропическими болезнями (PECET), http://www2.udea.edu.co/webmaster/indexudea.html (University of Antioquia)
Активная фаза проекта распределенных вычислений «Поиск лекарства от лейшманиоза» (Drug Search for Leishmaniasis, DSFL) под эгидой World Community Grid закончилась год назад, и с тех пор команда проекта обрабатывала полученные результаты, ранжировала и выбирала соединения, которые имеют наибольший потенциал оказаться кандидатами на эффективное лекарство от этой тяжелой тропической болезни.
Слева направо: Карлос Мускус Лопес из PECET; Фабио Кастелланос, менеджер IBM; Иван Велес, директор PECET
На данный момент обработано примерно 96% полученных данных, остальное должно быть завершено в ближайшие 2-3 недели. Исследователи практически завершили статью по итогам этой фазы работы, которая должна быть представлена в международных научных журналах до конца года. Для этого необходимо дождаться полных результатов обработки и фильтрации данных.
В прошлом году предварительные результаты проекта DSFL уже были представлены на различных местных, национальных и международных научных мероприятиях, в том числе на WorldLeish5 в Бразилии, Международном конгрессе паразитологии в Мехико и на XII-м Международном конгрессе по микробиологии в Картахене (Колумбия). Команда проекта DSFL также помогает с организацией III-го конгресса Колумбии по вычислительной биологии и биоинформатике, который состоится в сентябре 2015 г. в Медельине. Это будет прекрасная возможность представить результаты проекта DSFL в развернутом формате и способствовать дальнейшему продвижению World Community Grid в научной среде.
Планируется второй этап проекта, который будет ориентирован на исследования взаимодействия между лигандом (потенциальной лекарственной молекулой) и рецептором (ключевыми белками-целями, критичными для развития лейшманиоза). Сила этого взаимодействия может быть определена с помощью программы Метод анализа распределения энергии (Binding Energy Distribution Analysis Method, BEDAM) или другой аналогичной программы.
Волонтеры World Community Grid помогли в обработке в общей сложности 4 Тб данных, состоящих из более 1,5 миллиардов записей, которые хранят информацию об энергии взаимодействия между множеством белков лейшманиоза и библиотекой из 600 тысяч химических соединений. Воспоследовавшая перекомпиляция результатов расчетов была необходима для фильтрации и отбора наиболее релевантных данных. Полученная база данных была построена с информацией о целевых показателях математических моделей белков, полученной в ходе молекулярно-динамического моделирования их взаимодействия с молекулами лигандов, с оценкой энергии взаимодействия между участвующими молекулами. Целью этого первого этапа было ранжирование и отбор лучших кандидатов на основе мета-анализов, которые могли бы определить наиболее подходящие лиганды для последующих экспериментальных подтверждений.
Исследователи идентифицировали несколько критичных для лейшманиоза белков, которые и были широко изучены в качестве потенциальных молекулярных мишеней. Некоторые из них продемонстрировали в ходе имитационных расчетов высокие свободные энергии взаимодействия (ок. -13 ккал/моль) с перспективными лигандами (см. http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/about_us/viewNewsArticle.do?articleId=400). Предварительные результаты показывают, что возможно найдены потенциально эффективные кандидатные лекарственные соединения от лейшманиоза, которые могут быть улучшены в ходе дополнительных вычислительных и экспериментальных подтверждений.
Исследователи готовятся ко второй стадии проекта, которая включает в себя дополнительный фильтр отбора с использованием улучшенного ПО для молекулярно-динамического моделирования, чтобы избежать ложных срабатываний и, следовательно, обнаружить кандидатные соединения с более высокими шансами на дальнейшее превращение в лекарственные препараты. Задача минимум стоит в подтверждении, по крайней мере, одной эффективной лекарственной молекулы, способной бороться с лейшманиозом без серьезных побочных эффектов для организма.
Теперь, когда почти закончен анализ результатов моделирования потенциальных соединений, должен состояться переход к реальному тестированию для подтверждения прогнозных оценок. Это требует больших финансовых затрат на лабораторные исследования и материалы. К сожалению, исследователи столкнулись с трудностями обеспечения финансирования этих работ, несмотря на многочисленные заявки в международные научные фонды. На сегодняшний день они не увенчались успехом, поэтому от идеи провести тестирование всех перспективных соединений пришлось отказаться. Однако, главное колумбийское агентство по финансированию научных разработок (Colombian funding agency – Colciencias) утвердило выделение средств для тестирования от 10 до 20 соединений. Десять из наиболее перспективных соединений уже приобретены и проходят испытания в нашей лаборатории. Лучшие из них пройдут испытания на животных перед клинической фазой испытаний на людях.
Доктор Карлос Лопес от лица коллектива проекта DSFL выражает особую благодарность команде объединения World Community Grid за оказываемую помощь, а также всем участникам распределенных вычислений, которые предоставили свои вычислительные ресурсы для проекта. До новых встреч!
28 ноября 2014
Подготовлено http://distributed.org.ua по материалам World Community Grid: http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/about_us/viewNewsArticle.do?articleId=400
Автор: re_SET Dec 9 2014, 20:50
От лица себя любимого, и (я надеюсь команда не против) всех кранчеров нашей дружной команды хочу выразить благодарность нашему кранчеру ("Арбалет") за хорошо проведенную работу по поиску и переводу статьи выше ![]() . Спасибо Тебе большое, друже!
. Спасибо Тебе большое, друже! ![]()
Автор: Arbalet Dec 9 2014, 20:56
re_SET ![]()
Да как-то сам не ожидал от себя такой прыти - в руках все горит, как в старые-добрые времена ![]()
![]()
Будем надеяться, что исследователи из проекта DSFL доведут работу до конца и все-таки получат новое лекарство от этой вредной болячки!
Invision Power Board
© Invision Power Services
