Привіт Гість ( Вхід | Реєстрація )
| Rilian |
 Jun 18 2007, 16:31 Jun 18 2007, 16:31
Пост
#1
|
 interstellar           Група: Team member Повідомлень: 17 399 З нами з: 22-February 06 З: Торонто Користувач №: 184 Стать: НеСкажу Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: ноут и кусок сервера |
 Проект занимается подбором лекарств от ВИЧ * Официальный сайт * Прогресс и статус исследований на официальном сайте Как присоединиться читайте в главном топике World Community Grid Подробнее о научных методах в FightAIDS@Home: Белки, как вы уже знаете, является строительным материалом для всех живых существ. Разнообразные формы белков принимают участие во всех процессах, происходящих в живых организмах. Белки являются длинными цепями меньших молекул - аминокислот. Энзимы являются конкретными типами белков, которые ускоряют биохимические реакции. Протеаза - энзим, который способен «вырезать» отдельный белок в некоторой точке аминокислотной цепи. Например, когда Вы едите пищу, которая также содержит белок, белковые молекулы режутся на меньшие аминокислотные молекулы протеазой в вашем желудке. Ваш организм может затем использовать получившиеся аминокислоты, чтобы формировать белки, которые ему нужны для продолжения жизнедеятельности. Стоит отметить также, что только небольшой процент из всех белков в организме является протеазами, поэтому эти белки очень важны в своем функционировании для обеспечения жизненных процессов. Ваш компьютер поможет нам имитировать процесс присоединения множества различных лиганд* к HIV-протеазе (HIV- Human Immunodeficiency Virus – вирус иммунодефицита человека), для этого используется компьютерная программы под названием AutoDock. *Лиганды - (от лат . ligo - связываю), в комплексных соединениях молекулы или ионы, связанные с центральным атомом (комплексообразователем), напр. в соединении [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 центральный атом - Со, а лиганды - молекулы NH3. Перспективные лиганды будут изучены более подробно учеными, и это должно привести нас к созданию лекарства для управления ВИЧ-инфекцией, и в конце концов, к предотвращению заболевания СПИДОМ. Естественно, моделирование таких процессов – сложная в вычислительном отношении задача из-за большого разнообразия белковых структур и выделению из них тех, которые могут эффективно повлиять на вирус, поэтому в данном проекте также используются методы распределенных вычислений. QUOTE What is AIDS? UNAIDS, the Joint United Nations Program on HIV/AIDS, estimated that in 2004 there were more than 40 million people around the world living with HIV, the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. The virus has affected the lives of men, women and children all over the world. Currently, there is no cure in sight, only treatment with a variety of drugs. Prof. Arthur J. Olson's laboratory at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) is studying computational ways to design new anti-HIV drugs based on molecular structure. It has been demonstrated repeatedly that the function of a molecule — a substance made up of many atoms — is related to its three-dimensional shape. Olson's target is HIV protease ("pro-tee-ace"), a key molecular machine of the virus that when blocked stops the virus from maturing. These blockers, known as "protease inhibitors", are thus a way of avoiding the onset of AIDS and prolonging life. The Olson Laboratory is using computational methods to identify new candidate drugs that have the right shape and chemical characteristics to block HIV protease. This general approach is called "Structure-Based Drug Design", and according to the National Institutes of Health's National Institute of General Medical Sciences, it has already had a dramatic effect on the lives of people living with AIDS. Even more challenging, HIV is a "sloppy copier," so it is constantly evolving new variants, some of which are resistant to current drugs. It is therefore vital that scientists continue their search for new and better drugs to combat this moving target. Scientists are able to determine by experiment the shapes of a protein and of a drug separately, but not always for the two together. If scientists knew how a drug molecule fit inside the active site of its target protein, chemists could see how they could design even better drugs that would be more potent than existing drugs. To address these challenges, World Community Grid's FightAIDS@Home project runs a software program called AutoDock developed in Prof. Olson's laboratory. AutoDock is a suite of tools that predicts how small molecules, such as drug candidates, might bind or "dock" to a receptor of known 3D structure. The very first version of AutoDock was written in the Olson Laboratory in 1990 by Dr. David S. Goodsell, since then, newer versions, developed by Dr. Garrett M. Morris, have been released which add new scientific understanding and strategies to AutoDock, making it computationally more robust, faster, and easier for other scientists to use. From the beginning of this project, World Community Grid has been running a pre-release version of AutoDock4. In August 2007, World Community Grid started running the new publicly available version 4 of AutoDock which is faster, more accurate, can handle flexible target molecules and thus can also be used for protein-protein docking analysis. AutoDock is used in the FightAIDS@Home project on World Community Grid to dock large numbers of different small molecules to HIV protease, so the best molecules can be found computationally, selected and tested in the laboratory for efficacy against the HIV virus. By joining forces together, The Scripps Research Institute, World Community Grid and its growing volunteer force can find better treatments much faster than ever before.  График проекта  Ссылки ВИЧ 3D Це повідомлення відредагував Rilian: Sep 8 2010, 11:49 |
  |
Відповідей(60 - 74)
| Rilian |
 Feb 11 2009, 23:38 Feb 11 2009, 23:38
Пост
#61
|
 interstellar           Група: Team member Повідомлень: 17 399 З нами з: 22-February 06 З: Торонто Користувач №: 184 Стать: НеСкажу Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: ноут и кусок сервера |
QUOTE The FAAH Project Status Page on the The Scripps Research Institute website was updated on 9 February 2009. New experiments, numbered 25, 26 and 27 have been outlined. These will comprise WU batches faah5224-5709. According to the updated info, we still have to crunch 49% of Experiment 22, which comprises WU batches faah4417-4622 and faah5018-5223, and which we're crunching now. The fact that we're currently running batches around faah5167 would suggest that we are more than 51% through this experiment, though. Also outstanding are 5% of Experiment 23 and 2% of Experiment 21. [quote]The Статус проекта FAAH на сайте The Scripps Research Institute был обновлен 9 февраля 2009. Появилась информация о новых экспериментах, 25, 26 и 27, которые соответствуют будущим пачкам ВЮ faah5224-5709. Согласно обзору, все еще необходимо досчитать 49% эксперимента 22 (ВЮ faah4417-4622 и faah5018-5223). Сейчас сервер раздает ВЮ faah5167 поэтому можно предположить что 51% уже посчитан. Также осталось досчитать и перепроверить 5% эксперимента 23 и 2% эксперимента 21 Подробнее об экспериментах на английском: Experiment 27: 0% Completed This experiment utilizes the same set of brand new crystal structures and new models of HIV protease that are being used in Experiments 25 and 26. See the description of Experiment 25 for the details about these new targets. In experiment 27, we are targeting the exo site on the sides of HIV protease. This experiment incorporates a library of ligands that we have never used before. We recently downloaded and reformatted the "ChemBridge building blocks library" of ~ 12,000 models of compounds from "ZINC," (which stands for Zinc Is Not Commercial). See the paragraph below for a few details about ZINC. The library of "building blocks" from ChemBridge contains many small fragments that were derived from larger compounds. Using these small fragments, or building blocks, should help us cover a larger amount of structural diversity (i.e., of "chemical space") within each experiment. Thus, this library should help us find new hits in a more efficient way. Kudos to ZINC! The virtual representations of the potential inhibitors that we use in all of these experiments are derived from the libraries of ligands that are freely distributed by "ZINC," (which stands for Zinc Is Not Commercial). ZINC is a free database provided by the Shoichet Laboratory in the Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF). To learn more about ZINC, see Irwin, J. and Shoichet, B. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005; 45(1):177-82. We thank Dr. John Irwin and Prof. Brian Shoichet for creating and maintaining such a wonderfully useful and free site. Experiment 26: 0% Completed Similar to Experiment 25, this experiment also involves screening the NCI's "DTP library of moderately active compounds" against several brand new structures and new models of HIV protease. But in this experiment, we are docking the potential inhibitors against the active site, instead of the exo site. See the description of Experiment 25 for the details regarding the new structures and models that we are targeting. Experiment 25: 0% Completed This experiment involves screening the NCI's "DTP library of moderately active compounds" against the exo site of several brand new structures and new models of HIV-1b protease. (See the description of "Experiment 21" for more details about this DTP library.) This experiment targets the potential allosteric inhibitor site (i.e., the "exo site") on the sides of HIV protease. The new structures utilized in this experiment are based on brand new, currently unpublished x-ray crystallographic structures from our collaborator, Prof. David Stout. The new models of HIV protease that are also included in this experiment were harvested from Molecular Dynamics simulations recently performed by Dr. Alex L. Perryman. We harvested the equilibrated structures from the beginnings of our new MD simulations on several different multi-drug-resistant mutants of HIV-1b protease (i.e., several different "super bugs" against which the current drugs no longer work well.) We also included models of HIV-1c protease ("1c" is the HIV subtype, or group of strains, that are most common in Asia) and HIV-2 protease ("HIV-2" is the predominant subtype in Africa). "HIV-1b" is the subtype of HIV most commonly found in the U.S. and in Europe. The current anti-AIDS drugs were all designed and optimized against HIV-1b, but the FightAIDS@Home project is devoted to trying to help all patients with HIV throughout the world. ------------- от себя добавлю, что вообще информация о текущих статусах и результатах проекта обновляется почти каждый месяц, что свидетельствует о действительной важности этих экспериментов в попытках борьбы со СПИДом. Второй большой плюс - избыточность проекта составляет < 1.2, то есть практически проверяется каждая пятая ВЮ. Остальные ВЮ уникальны -------------------- |
| nikelong |
 Feb 13 2009, 15:57 Feb 13 2009, 15:57
Пост
#62
|
|
Тера ранчер           Група: Trusted Members Повідомлень: 12 443 З нами з: 19-March 05 Користувач №: 92 Стать: Чол |
http://www.boinc-af.org/content/view/580/287/
http://www.boinc-af.org/content/view/667/219/ http://www.dp.by/wiki/Projects/Fightaidsathome http://www.fightaidsathome.ru/pressa.htm http://www.ibm.com/news/fr/fr/2005/11/cp1793.html -------------------- |
| Rilian |
 Sep 26 2009, 16:55 Sep 26 2009, 16:55
Пост
#63
|
 interstellar           Група: Team member Повідомлень: 17 399 З нами з: 22-February 06 З: Торонто Користувач №: 184 Стать: НеСкажу Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: ноут и кусок сервера |
Получил изумрудную медаль за 1 год процессорного времени:
 -------------------- |
| tribal |
 Sep 26 2009, 21:51 Sep 26 2009, 21:51
Пост
#64
|
 Kранчер из глубинки        Група: Trusted Members Повідомлень: 933 З нами з: 16-October 08 З: Горловка Користувач №: 845 Стать: Чол Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: AMD Athlon II X4 635@3.3GHz/ GF250GTS |
Rilian
--------------------  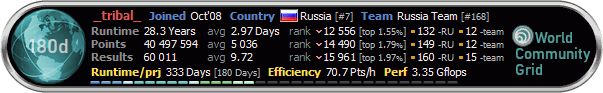 |
| Abbath |
 Sep 28 2009, 23:07 Sep 28 2009, 23:07
Пост
#65
|
 kранчер     Група: Trusted Members Повідомлень: 77 З нами з: 11-February 07 З: Кмев Користувач №: 438 Стать: Чол Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: Core2Duo 4400@2.4GHz + Core Duo T2400 1.83GHz |
а.. вот оно что.. и у меня такая есть.. а я все думал куда дели золотую медаль, подсунув какую то муть зеленую )
-------------------- |
| Rilian |
 Nov 4 2009, 09:41 Nov 4 2009, 09:41
Пост
#66
|
 interstellar           Група: Team member Повідомлень: 17 399 З нами з: 22-February 06 З: Торонто Користувач №: 184 Стать: НеСкажу Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: ноут и кусок сервера |
03 Nov 2009 – FightAIDS@Home Project Update - Volume 8
http://fightaidsathome.scripps.edu/images/FAAHvol8.pdf -------------------- |
| Rilian |
 Feb 9 2010, 03:19 Feb 9 2010, 03:19
Пост
#67
|
 interstellar           Група: Team member Повідомлень: 17 399 З нами з: 22-February 06 З: Торонто Користувач №: 184 Стать: НеСкажу Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: ноут и кусок сервера |
Status update - http://fightaidsathome.scripps.edu/status
Project Status, as of February 8, 2010 Experiment 31: 52% Completed Experiment 31 involves screening the Otava library of approximately 335,000 "building blocks" against the "exo sites" on the side surfaces of HIV protease (i.e., the allosteric sites). This experiment will dock these fragments against the exo sites of 8 different targets, which include 5 carefully-selected snapshots from previous Molecular Dynamics simulations of the V82F/I84V multi-drug-resistant mutant "super bug." The other targets correspond to the two new fragment-bound crystal structures of HIV protease that were produced by our collaborator, Prof. C. David Stout at TSRI. We are targeting both sides of one of these two new targets, which is why we have "8 different targets." These two new structures from Prof. Stout were also targeted in Experiments 25-28 and 30. This experiment involves faah8972 - faah11646. These calculations began 12/07/2009. Experiment 30: 100% Completed Like Experiment 29, Experiment 30 also uses the "Asinex" library of over 360,000 different compounds in a virtual screen against HIV protease. But in this experiment, the Asinex compounds are being docked against the allosteric inhibitor site (that is, the "exo site" on the sides of HIV protease). In addition, this experiment targets two new fragment-bound crystal structures of protease that were produced by our collaborator, Prof. C. David Stout at TSRI. These two new structures from Prof. Stout were also targeted in Experiments 25-28. This experiment involves faah8234 - faah8971. These calculations began 10/05/2009 and ended 12/07/2009. Experiment 29: 100% Completed This experiment involves docking a huge library of compounds against the active site of six of our new models of HIV protease (which are a subset of the targets being used in Experiments 25-27). These six targets are the outputs of the equilibration phase of six different Molecular Dynamics simulations (hence the "mdEq" part of the work units' names). The six different types of HIV protease that we are docking compounds against in Exp. 29 include the "Model6Xapo," which is a drug-resistant "super bug" with 6 different mutations. Our collaborator, Prof. Dave Stout, figured out the structure of this 6X mutant. The "apo" part of the name indicates that this mutant protease molecule did not have a substrate or drug present when its structure was solved. This Model6Xapo has semi-open flaps (that is, the two double-arrows that point towards the center of the molecule and form a roof over the active site have opened up). We've been working with the IBM members of the FAAH team to update the graphics on your screen-savers. We've sent them new graphics to use, and they've already started testing them. Soon, you will be able to see exactly what we mean when we say "semi-open flaps." Another new model that is being targeted in Exp. 29 is the wild type HIV protease from 1HHP.pdb. We consider this model to be interesting, because the flaps were fairly open, but then they closed again. But this time, they closed down in the opposite arrangement/they "switched handedness" (that is, the flap that is normally in the front is now in the back). Having this different conformation of the flaps might allow us to fish out new types of interesting compounds for subsequent examination in the "test tube." We included models of a multi-drug-resistant "super bug" with mutations at V82F/I84V and another "super bug" with mutations at I62V/V82A/I84V/L90M. We are targeting a model of the protease molecule from "HIV-1c," as well. HIV-1c is the subtype, or group of strains, that is most commonly found in Asia. We are also targeting a model of "HIV-2" protease with semi-open flaps. HIV2 is the group of strains that are most commonly found in Africa. The current anti-AIDS drugs were developed and optimized against "HIV-1b," which is the subtype most commonly found in Europe and the USA. But some of these anti-HIV protease drugs do not work as well against even the wild type strains that are found in other regions (let alone their "super bugs"). Since we are not controlled by the desire to make profit, we are devoting some of our research efforts to the groups of HIV strains that affect the often-neglected patients in Africa and Asia. In addition, studying these versions of HIV protease can also help us learn how to defeat the "super bugs" we find here in the USA. This experiment is the first one in which we are using the "Asinex" library of over 360,000 different compounds in our virtual screens against HIV protease. This experiment involves faah6022-faah8233. These calculations began 4/23/2009 and ended 10/20/2009. Experiment 28: 100% Completed This experiment utilizes the same set of brand new crystal structures and new models of HIV protease that are being used in Experiments 25-27. See the description of Experiment 25 for the details about these new targets. In experiment 28, we are AutoDocking these compounds against the active site of different variants of HIV protease. This experiment incorporates a library of ligands that we just started using: the ChemBridge building blocks library. The library of "building blocks" from ChemBridge contains many small fragments that were derived from larger compounds. Using these small fragments, or building blocks, should help us cover a larger amount of structural diversity (i.e., of "chemical space") within each experiment. Thus, this library should help us find new hits in a more efficient way. This experiment involves faah5710-6021. These calculations began 4/05/2009 and finished 4/24/2009. -------------------- |
| Rilian |
 Mar 8 2010, 18:43 Mar 8 2010, 18:43
Пост
#68
|
 interstellar           Група: Team member Повідомлень: 17 399 З нами з: 22-February 06 З: Торонто Користувач №: 184 Стать: НеСкажу Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: ноут и кусок сервера |
Ученые выяснили, что вирус иммунодефицита человека (ВИЧ), избегает уничтожения и выведения из организма человека, так как имеет возможность инфицировать клетки костного мозга.
Именно в них вирус "пережидает" воздействие лекарств, что может быть использовано для разработки новых методик лечения СПИДа, сообщается в статье исследователей, опубликованной в он-лайн выпуске журнала Nature Medicine. Открытие ученых позволило впервые объяснить многолетние неудачи медиков, разрабатывающих лекарства для уничтожения и выведения вируса из организма человека. Несмотря на большой прогресс в этой области, и разработку лекарств, после применения которых вирус в крови зараженного человека обнаружить не удается даже с помощью самых чувствительных методик, спустя некоторое время после прекращения употребления лекарства он снова оказывается в крови. Подробнее на МЕМБРАНе - http://www.membrana.ru/lenta/?10175 -------------------- |
| Rilian |
 Mar 17 2010, 23:04 Mar 17 2010, 23:04
Пост
#69
|
 interstellar           Група: Team member Повідомлень: 17 399 З нами з: 22-February 06 З: Торонто Користувач №: 184 Стать: НеСкажу Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: ноут и кусок сервера |
Обновлен статус проекта (тема на официальном форуме)!
Experiment 31: 77% Completed Experiment 31 involves screening the Otava library of approximately 335,000 "building blocks" against the "exo sites" on the side surfaces of HIV protease (i.e., the allosteric sites). This experiment will dock these fragments against the exo sites of 8 different targets, which include 5 carefully-selected snapshots from previous Molecular Dynamics simulations of the V82F/I84V multi-drug-resistant mutant "super bug." The other targets correspond to the two new fragment-bound crystal structures of HIV protease that were produced by our collaborator, Prof. C. David Stout at TSRI. We are targeting both sides of one of these two new targets, which is why we have "8 different targets." These two new structures from Prof. Stout were also targeted in Experiments 25-28 and 30. This experiment involves faah8972 - faah11646. These calculations began 12/07/2009. -------------------- |
| Rilian |
 Mar 29 2010, 12:35 Mar 29 2010, 12:35
Пост
#70
|
 interstellar           Група: Team member Повідомлень: 17 399 З нами з: 22-February 06 З: Торонто Користувач №: 184 Стать: НеСкажу Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: ноут и кусок сервера |
Обновлен статус проекта и описание следующего эксперимента
Project Status, as of March 16, 2010 Experiment 32: 0% Completed Experiment 32 involves screening the Otava library of approximately 335,000 "building blocks" (i.e., fragments) against the active site of 7 different versions of HIV protease. All but one of these target conformations were generated by Dr. Alex L. Perryman's Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations of 5 different variants of HIV protease. These 7 targets include 2 snapshots of the V82F/I84V mutant from ALP's 2004 paper in Protein Science. These 2 snapshots of a multi-drug-resistant "superbug" have semi-open conformations of the flaps, which makes these models good targets for the "eye site" that is located between the tip of a semi-open flap and the top of the wall of the active site. The 3rd target is the equilibration MD (EqMD) output for 1HSI.pdb, which is a semi-open conformation of HIV-2 protease. HIV-2 is the group of strains of HIV that are most common in Africa. We'll be targeting the "eye site" of 1HSI, as well. The 4th target is the EqMD output from 1MSN.pdb, which was created using a different crystal structure of the V82F/I84V superbug. This model has a closed conformation of the flaps, which means that we'll be targeting the floor of the active site. The 5th target also has a closed conformation of the flaps, but this EqMD output is from 2R5P.pdb, which is the wild type HIV-1c protease. HIV-1c is the group of strains of HIV that are most commonly found in Asia. The 6th target has semi-open flaps, and it is the EqMD output from 1TW7.pdb, which is a superbug with the mutations L10I/D25N/M36V/M46L/I54V/I62V/L63P/A71V/V82A/I84V/L90M. We'll be targeting the eye site of this superbug, too. The 7th target is a crystal structure of the wild type HIV protease with 5-nitroindole bound in the eye site. This new crystal structure from Prof. C. David Stout's lab was presented in the Supporting Information for our recent article in Chemical Biology and Drug Design, vol. 75: 257-268 (March 2010). This new research article of ours was recently discussed in a press release on Science Daily The Protein Data Bank is located at http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/home/home.do. You can search the PDB using the 4 character codes listed above (i.e., before the .pdb suffix) to learn more about each of these targets. This experiment involves faah11647 - faah13,984. -------------------- |
| Rilian |
 Mar 29 2010, 21:51 Mar 29 2010, 21:51
Пост
#71
|
 interstellar           Група: Team member Повідомлень: 17 399 З нами з: 22-February 06 З: Торонто Користувач №: 184 Стать: НеСкажу Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: ноут и кусок сервера |
Hi Rickjb and fellow crunchers,
I always focus on keeping the queue full first, and then I take the time to update the experiment descriptions and % completion statistics on the Status page: http://fightaidsathome.scripps.edu/status Don't worry, we'll have no problems keeping the new jobs coming your way. I'm now preparing novel types of experiments, which will involve targeting our new dynamic models of HIV integrase. The new "eye candy" at the bottom of the Status page shows you a dynamic ensemble of our new models of the G140S/Q148H drug-resistant mutant of HIV integrase. It's one of the superbugs that we'll start screening against fairly soon. See: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20096702 for a description of these targets. Experiment 33 will most likely be our first FAAH experiment devoted to the HIV integrase system. We'll be searching for totally new classes of integrase inhibitors, as a way of advancing the design of new drugs that should work against the drug-resistant mutants of HIV integrase that are already appearing in the clinics. Thank you all very much for your help, Alex L. Perryman, Ph.D. -------------------- |
| Rilian |
 Apr 2 2010, 00:18 Apr 2 2010, 00:18
Пост
#72
|
 interstellar           Група: Team member Повідомлень: 17 399 З нами з: 22-February 06 З: Торонто Користувач №: 184 Стать: НеСкажу Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: ноут и кусок сервера |
Experiment 32 начался (подробнее смотреть выше)
-------------------- |
| Rilian |
 Apr 9 2010, 22:49 Apr 9 2010, 22:49
Пост
#73
|
 interstellar           Група: Team member Повідомлень: 17 399 З нами з: 22-February 06 З: Торонто Користувач №: 184 Стать: НеСкажу Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: ноут и кусок сервера |
к нам, кранчерам, это не относится, но если кто хочет получить файлы результатов докинга FightAIDS@home, обращайтесь:
QUOTE Hi Everybody, Throughout the last few years, we have been asked several times about whether we share these results, or whether we hide the data and keep it secret. As a result, a couple months ago we posted the details of our data sharing policy on the FAAH homepage and on the FAAH Status page: http://fightaidsathome.scripps.edu/ and http://fightaidsathome.scripps.edu/status At the bottom of each of the above pages, you can find the following description (in larger font size than the rest of the text): "Results of these FightAIDS@Home experiments are available to the public as raw, unprocessed AutoDock dlg files upon request. E-mail Dr. Alex L. Perryman at _______ for further information [follow the links above to find my address]. Please include the phrase "FAAH data" in the subject line of your e-mail. Since the amount of data is on the order of many terabytes, you will need to provide suitable media (such as external hard drives) for receiving a copy of these results." I just wanted to let you all know that when someone actually asks for a copy of the results of particular FAAH experiments, we share the data. Best wishes, Alex L. Perryman, Ph.D. Вот еще выложили какую-то новую картинку PS--I also added some new eye candy to the bottom of the Status page. I created this image of our new models of the G140S/Q148H drug-resistant mutant of HIV integrase using the free software PMV (Python Molecular Viewer), which is created, developed, and distributed by the Olson lab at TSRI.  Image above of an ensemble of target conformations of the G140S/Q148H drug-resistant mutant of HIV integrase was created by Alex Perryman. -------------------- |
| Rilian |
 Apr 22 2010, 11:46 Apr 22 2010, 11:46
Пост
#74
|
 interstellar           Група: Team member Повідомлень: 17 399 З нами з: 22-February 06 З: Торонто Користувач №: 184 Стать: НеСкажу Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: ноут и кусок сервера |
Experiment 32: 4% Completed
--- Experiment 33: 0% Completed Experiment 33 is our first FightAIDS@Home experiment that targets the HIV integrase system. While we are busy analyzing and extending the previous experiments you helped us perform against HIV protease, FAAH will now start screening compounds against the new dynamic models of wild type HIV integrase, the E92Q/N155H drug-resistant mutant, and the G140S/Q148H drug-resistant mutant that we recently created. We published these new models as the cover article for the March 26, 2010, issue of the Journal of Molecular Biology. An image of an ensemble of conformations (shapes) of the G140S/Q148H mutant is shown at the bottom of this page. Experiment 33 involves screening the "Asinex library" of over 360,000 different fragments and slightly larger compounds against our new dynamic models of the E92Q/N155H drug-resistant mutant of HIV-1 integrase. We are trying to identify compounds that can attach to brand new binding sites on this mutant. Thus, we are both searching for new types of inhibitors and for new, non-active site regions to which inhibitors can bind. We are screening these compounds against 6 different snapshots of this mutant that had the most open conformations of the "140s loop" near the active site. This loop is known to be critical to the catalytic function of integrase. This 140s loop is located in the top, left corner of the image at the bottom of this page. Since the 140s loop likely has a closed conformation during catalysis, we are searching for fragments that can stabilize the open, likely inactive conformations of the 140s loop. In other words, we are searching for fragments that might act as allosteric inhibitors (flexibility wedges that alter the shapes and motions sampled by this very flexible loop). The best compounds from this virtual screen will be assessed in test tubes, in assays performed by our collaborator Dr. Ying-Chuan Lin in Prof. John Elder's lab at TSRI. This experiment involves faah13,985 - faah16,198. -------------------- |
| Rilian |
 Apr 23 2010, 00:48 Apr 23 2010, 00:48
Пост
#75
|
 interstellar           Група: Team member Повідомлень: 17 399 З нами з: 22-February 06 З: Торонто Користувач №: 184 Стать: НеСкажу Free-DC_CPID Парк машин: ноут и кусок сервера |
Alex L. Perryman о будущих исследованиях FAAH - англ, много букв
по поводу Prototype Foamy Virus integrase CODE http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/forums/wcg/viewthread_thread,28346_lastpage,yes#277234 про HIV Vpu (viral protein U) CODE http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/forums/wcg/viewthread_thread,28717_lastpage,yes#277230 про banana lectin (лектин из бананов) CODE http://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/forums/wcg/viewthread_thread,5510_lastpage,yes#277242 -------------------- |
  |
1 Користувачів переглядають дану тему (1 Гостей і 0 Прихованих Користувачів)
0 Користувачів:

|
Lo-Fi Версія | Поточний час: 25th April 2024 - 01:25 |